Lasers in Medical Devices
Considering, Choosing, and Implementing Laser-Based Technology for Medical Devices
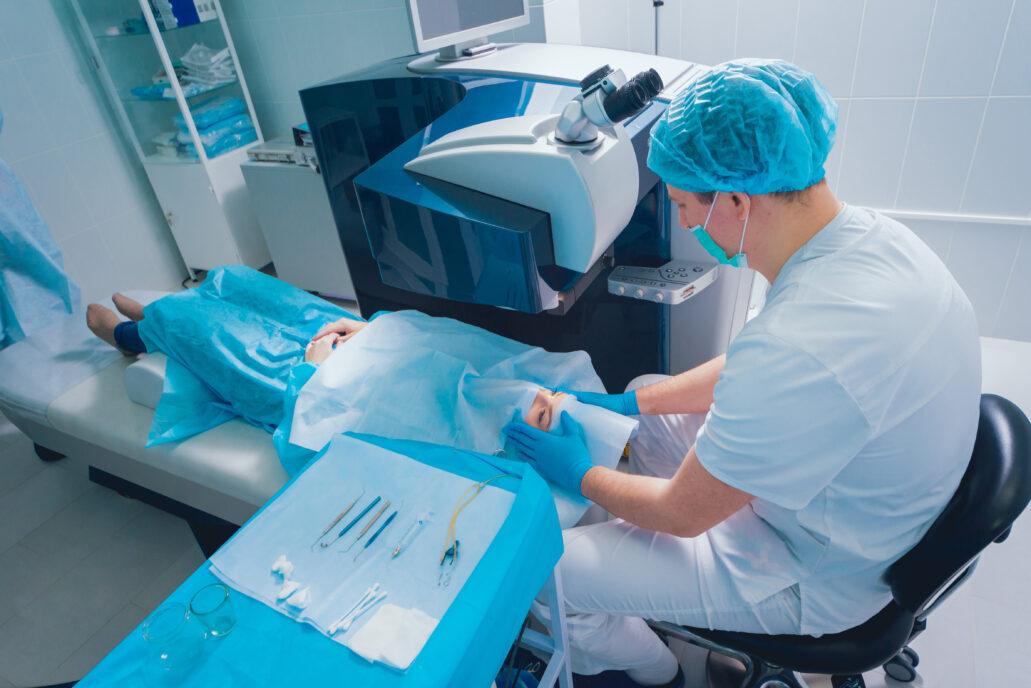
Over the last six decades, the use of lasers in medicine has grown rapidly. Lasers are now commonly used both as diagnostic tools and in various treatment modalities. This whitepaper is designed for readers considering, choosing, or implementing a laser-based technology in the device they are developing. It discusses the principles of operation of lasers, their useful properties, and their interactions with biological tissues, along with a non-exhaustive overview of the myriad ways in which they have been applied in medicine.
Since their inception, lasers have found applications in many medical specialties including dermatology, dentistry, ophthalmology, urology, and oncology, among others. Several unique properties of laser light (directionality, pulsed or continuous output, high peak and/or average powers, and long coherence times/lengths) make it applicable to many different diagnostic and treatment modalities. Lasers in medical devices can be a game-changer in the development process. They should be considered for use in cases where they can improve outcomes, reduce equipment costs, reduce patient recovery times, and/or reduce treatment times/costs.
For the reasons above, the market for medical lasers has continually expanded over the past six decades. The North American medical laser market was estimated to have a value of $1.87 billion USD in 2019, which is expected to more than double by 2027 (even after factoring in the effects of the COVID-19 pandemic). Lasers are now common in medical practice and will continue to be used for the indefinite future.
Lasers in Medical Devices
Considering, Choosing, and Implementing Laser-Based Technology for Medical Devices