
Axolotl BrainPrint Microsphere Generator
Axolotl Biosciences providing high-quality reagents for 3D printing human tissue models
3D bioprinting enables the creation of functional human tissues on demand, and it is suitable for various applications in repairing the human body as well as orthogonal applications such as drug screening. Axolotl’s BrainPrint microsphere generator is a commercial scale and high-throughput microfluidic production system for drug-releasing microspheres necessary to produce bioink for 3D tissue bioprinting.
Two novel Axolotl Biosciences bioink formulations (TissuePrint and BrainPrint) generate reproducible and functional human tissues derived from stem cells. BrainPrint contains drug-encapsulated microspheres, maintains high levels of cellular viability post-printing, and promote cellular differentiation into stable, mature neural tissues similar to those found in the brain. They are cheaper and require less labour than traditional tissue engineering and other commercially available bioinks.
Axolotl Biosciences is a privately owned company that spun-off of a bio-printing-focused research group led by Dr. Stephanie Willerth at the University of Victoria.
Axolotl needed microfluidics expertise
Scaling up production of the drug-releasing microspheres while maintaining the required size and drug encapsulation efficiency of the microspheres needed microfluidics commercialization expertise. Major challenges for transfer to manufacturing were finding a chemically compatible material for the device and a suitable manufacturing technique.
Axolotl turned to StarFish for support across the whole project
With funding support from Next Generation Manufacturing Canada (NGen), Axolotl engaged StarFish Medical to implement high-throughput microfluidic processes for fabricating these drug-releasing microspheres based on prototypes developed in the Willerth and Elvira labs at the University of Victoria.
StarFish supported Axolotl with a an array of deliverables and support services including the following:
- Designing prototype microfluidic cartridge using analytical and numerical analysis and computational fluid dynamics simulations of droplet generation parameters to reduce physical prototyping development costs.
- Developing prototype microfluidic cartridges in-house for the proof of concept.
- Designing the manufacturing process to ensure microfluidic cartridges were optimized for scale-up and capable of producing microspheres to specification.
- Developing and implementing a quality control processes for Axolotl’s novel BrainPrint bioink as well as conducting beta testing to ensure viability as a trusted commercial product.
- Supporting Axolotl with its regulatory submission activities.
StarFish and Axolotl worked together
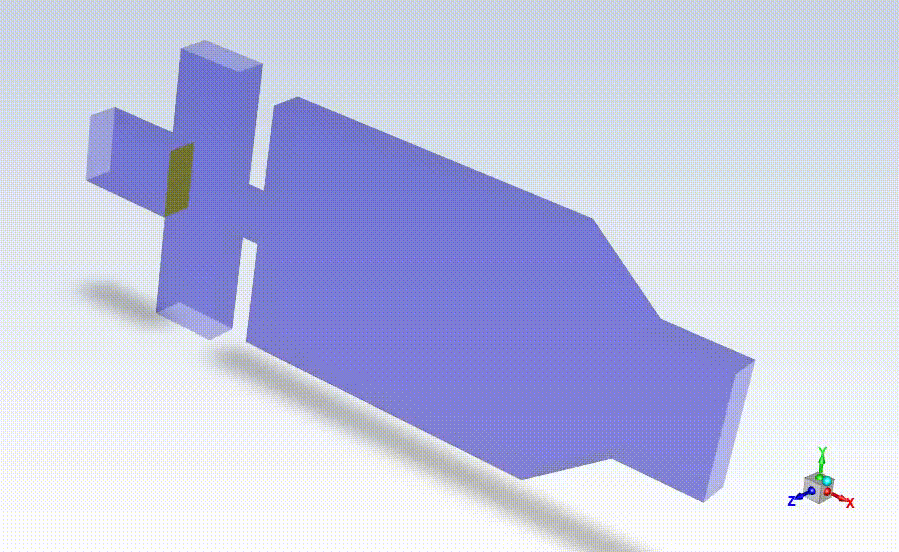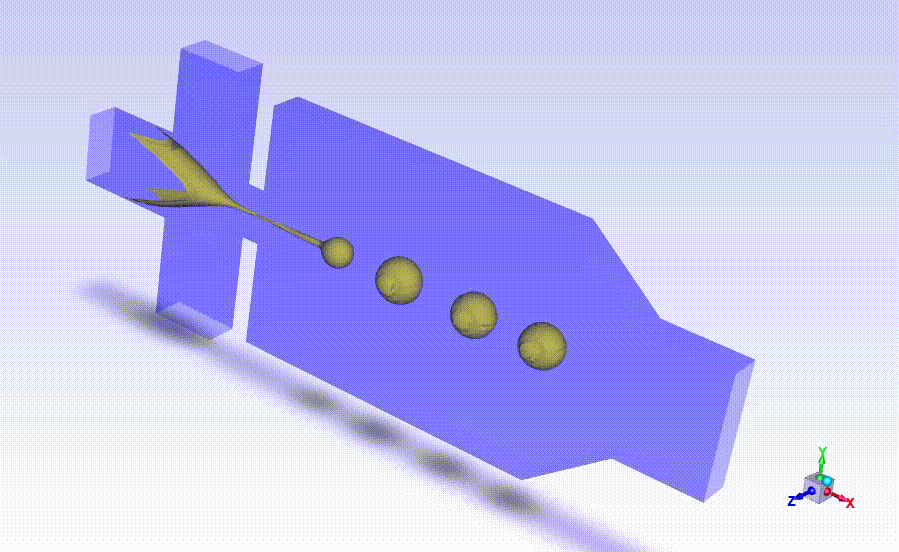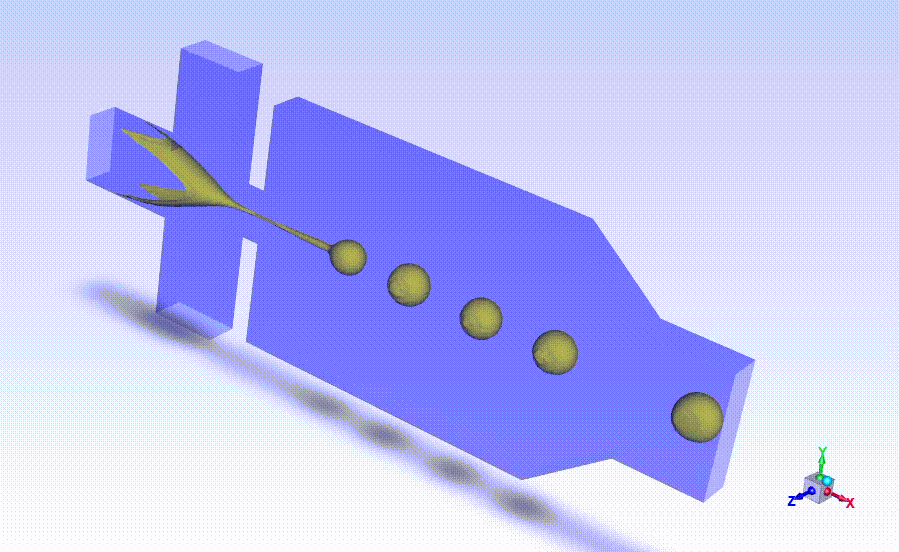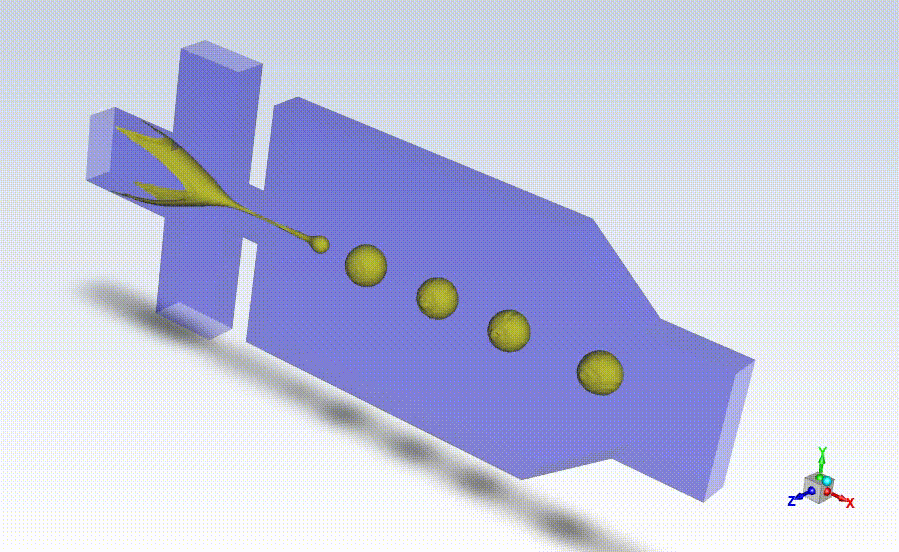
Working closely with StarFish, Axolotl coordinated beta testing and evaluation of the BrainPrint bioink to adapt the preliminary device prototype into a design suitable for manufacturing larger quantities of the drug-releasing microspheres for commercial use. StarFish then designed prototypes using the SolidWorks platform and manufactured them in-house using a high-precision Computer Numerical Control (CNC) machine (MDA precision), and a BossLaser laser cutter for assembly.
With the prototypes built and verified by Axolotl, StarFish Medical developed manufacturing transfer plans taking into consideration all risk factors associated with the manufacturing.
Designs were presented to microfluidics manufacturers and divided into categories based on low- and high- volume production then evaluated according to the manufacturing techniques and materials used by each manufacturer. This approach informed the supply chain management and resulted in timely resourcing.
Results
- Two microfluidic concepts and prototypes that can produce drug-releasing microspheres with the desired output volume and microsphere specifications.
- Novel technique to seal aluminum and Peek microfluidic cartridges while maintaining optical transparency.
- Design transfer to manufacturing.