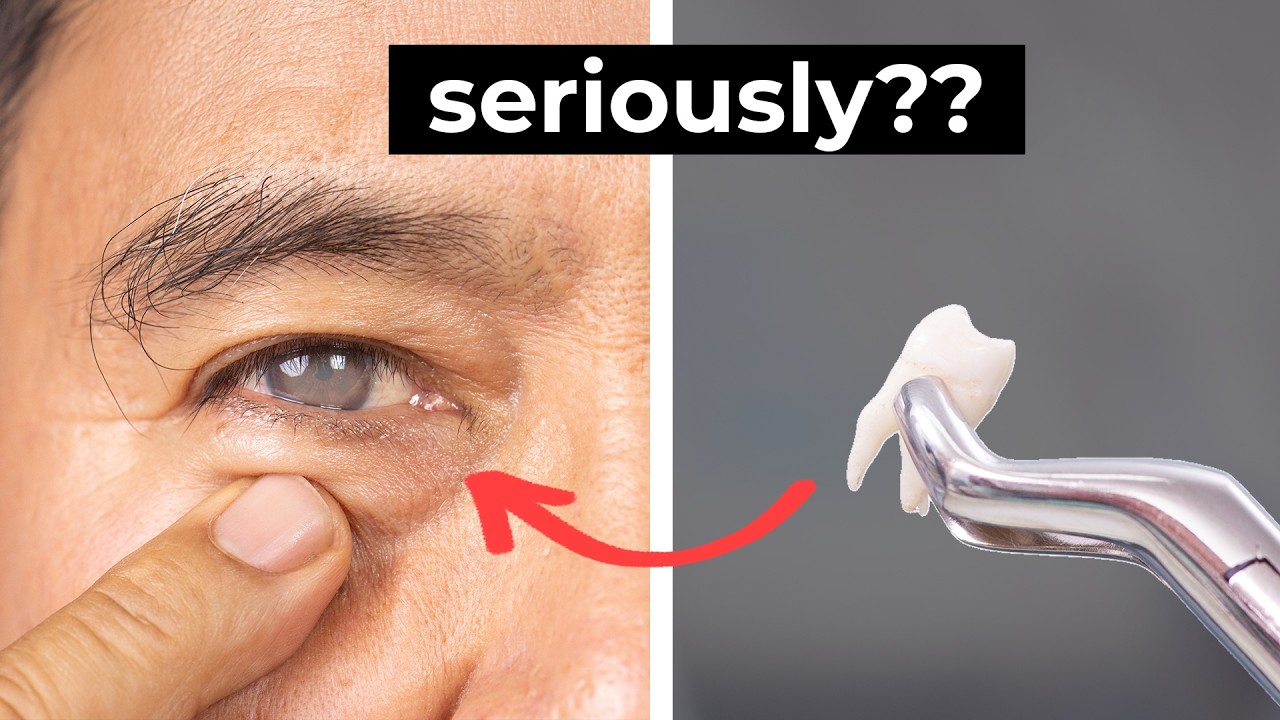
Bio Break: Tooth-In-Eye Surgery
In this episode of Bio Break, Nick Allan and Joris van der Heijden dive into one of the most astonishing medical innovations we’ve ever come across: osteo-odonto-keratoprosthesis. Or, as Nick quickly dubs it, “tooth in eye surgery.”
This fascinating procedure sounds like science fiction but has been successfully used to restore vision in people who are blind due to damage in the front part of the eye, such as from trauma or autoimmune diseases. While the retina remains functional, traditional options are off the table. That’s where this extreme innovation comes in.
Joris explains how the procedure starts with removing a patient’s tooth and some surrounding bone to create a small square-shaped structure. A hole is drilled in the center, and a tiny lens is implanted, this piece will eventually act as an artificial cornea. But before it’s implanted into the eye, it needs to be biologically prepared. That’s done by temporarily placing the implant into the patient’s cheek, where it can become vascularized over a few months.
Once ready, the patient returns to the hospital for the second stage. Surgeons retrieve the now-living implant from the cheek and carefully insert it into the eye, replacing the damaged corneal area. Thanks to the previously grafted oral tissue, the eye is prepped to accept the implant, and the result is stunning: restored vision in up to 90% of patients.
Even more impressive? Around 50% of these individuals gain high-quality vision, enough to read or even consider driving.
Whether you’re a medtech enthusiast or just love mind-blowing medical stories, this episode is a must-watch. Learn how combining dental tissue, ocular surgery, and a bit of clever biology can give people their sight back.
Tooth-In-Eye Surgery
Five Eye Diseases linked to majority of blindness or poor vision.
Related Resources

Computer vision technologies such as convolutional neural networks and vision transformers are transforming how AI analyzes medical images, each offering distinct advantages depending on the application and computing environment.

Ariana and Mark explore how prototype strategy helps teams reduce technical risk and accelerate progress.

Antibiotics changed medicine forever, but many people still wonder how penicillin works at a biological level. Nick and Nigel break down the science behind one of the most important antibiotics ever discovered.
I was recently looking through the OPTICA trade journal Optics and Photonics News – specifically its summary of “Optics in 2025.” A few highlights were of particular interest to me in terms of their potential applicability to future medical devices.