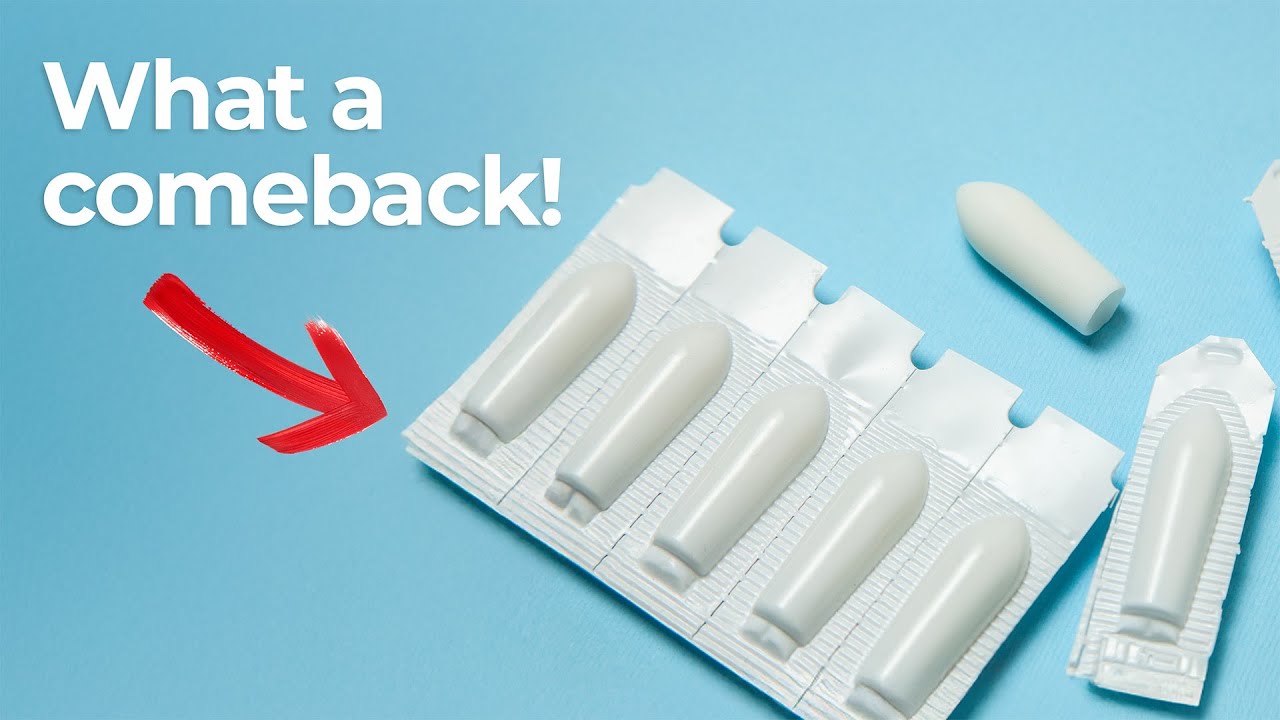
Suppository Drug Delivery Is Making a Comeback
In this episode of Bio Break, Nick and Nigel explore one of the oldest and most underappreciated drug delivery methods in modern medicine: the suppository. While often the subject of light humor, suppository drug delivery is gaining serious attention in the MedTech world for its effectiveness, ease of use, and broad applicability.
What Makes Suppositories Effective?
Suppositories are an example of non-oral drug delivery that bypasses the gastrointestinal system’s complex environment. Unlike oral tablets, which are subject to breakdown in the stomach and first-pass metabolism in the liver, suppositories can deliver medication directly into the bloodstream. This can lead to faster onset of action and greater bioavailability for certain drugs.
They’re particularly useful in scenarios where oral administration isn’t practical—such as when a patient is unconscious, vomiting, or otherwise unable to swallow medication. For these cases, suppository drug delivery provides a reliable and safe alternative.
Versatility in Drug Delivery
Suppositories are well-known for treating localized issues like hemorrhoids and constipation, but their role in systemic delivery is expanding. The slow-melting base at body temperature enables steady absorption, which can be ideal for sustained-release applications.
Nick and Nigel highlight the growing interest in advanced formulations like liposomes, nanoparticles, and mucoadhesives. These allow for more targeted delivery, longer duration of action, and better retention in mucosal tissues. Some formulations use thermosensitive materials that stay solid at room temperature but activate upon insertion—further enhancing delivery control.
A Resurgent Interest
According to Nick, the market for suppository-based drug delivery is growing, supported by promising research and real clinical needs. With an estimated 10% annual growth rate, this method is proving its value in both emerging therapies and everyday healthcare.
While suppositories may seem elementary, they continue to evolve—offering a reliable, low-cost solution in the right therapeutic context.
Learn more about StarFish Medical.
Related Resources
Nick and Nigel walk through how sterile disposables are processed and verified before they reach the field.
The FDA agentic AI is making headlines after the agency announced its own internal AI review tool. In this episode of MedDevice by Design, Ariana and Mark discuss what this could mean for medical device submissions and regulatory efficiency.

The sandwich ELISA assay is one of the most common ELISA formats used in diagnostics. Nick and Nigel walk through the method step by step using simple visuals and plain language.