
Bio Break: The Role of Pipettes in Lab Workflows
In this episode of Bio Break, Nick and Joris dive into a common challenge faced by researchers and product developers: the use of pipettes in laboratory workflows and the need for alternatives in non-laboratory environments. From the precision of the trusty P200 pipette to innovative solutions like microfluidics, this discussion highlights the strengths and limitations of fluid handling tools in research and beyond.
Nick kicks things off by showcasing his favorite instrument, the P200 pipette. Renowned for its precision and ease of use, the pipette is a cornerstone in basic research, capable of transferring fluids in the range of 1–200 microliters. With its ergonomic design and disposable tips, it ensures accuracy and contamination-free sample handling, making it indispensable for laboratory scientists. However, as Joris points out, transitioning workflows out of the lab introduces unique challenges.
The conversation shifts to why developers and clients often seek alternatives to pipettes. For instance, in clinical or point-of-care settings, pipettes may not be practical due to operator inexperience or the need to handle viscous solutions like honey or biological samples. Nick illustrates this challenge with a viscosity comparison, explaining how materials like honey, with viscosity 1,000 times that of water, are difficult to handle using traditional pipettes.
Joris introduces innovative alternatives like microfluidics, a precise and controlled method for transporting small liquid volumes, and off-the-shelf transfer pipettes, which can be cost-effective but may lack the precision required for critical applications. These solutions showcase the importance of adapting workflows to specific needs, whether it’s improving accuracy, handling viscous fluids, or operating in non-lab environments.
Whether you’re a researcher, engineer, or product developer, this episode provides valuable insights into optimizing fluid handling for various scenarios. Learn about the trade-offs of replacing pipettes and how cutting-edge tools can transform workflows.
The Role of Pipettes in Lab Workflows
Related Resources
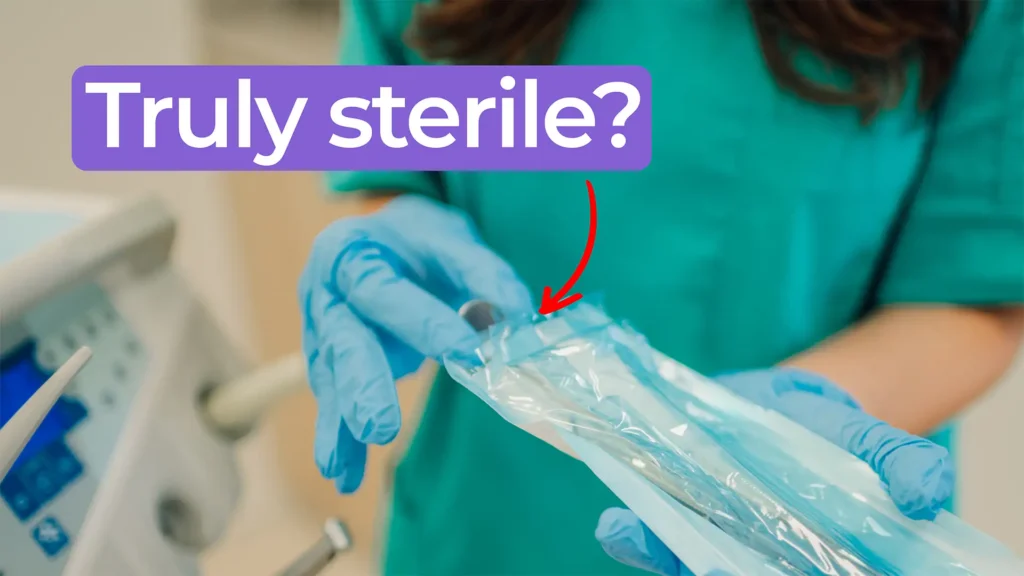
Nick and Nigel walk through how sterile disposables are processed and verified before they reach the field.

The sandwich ELISA assay is one of the most common ELISA formats used in diagnostics. Nick and Nigel walk through the method step by step using simple visuals and plain language.

Nick and Nigel walk through how indirect ELISA works, why it uses two antibodies instead of one, and when this approach makes the most sense in real diagnostic workflows.

Nick and Nigel break down the ELISA assay explained in simple, practical terms using everyday models.
