Resource Centre
Discover a wealth of knowledge and insights from the experts at StarFish Medical. Our Resource Centre offers product development tips, reviews of new and cutting-edge technologies, and in-depth articles on regulatory updates and compliance in medical device development.
-

Mark Drlik and Ariana Wilson introduce the fascinating world of ingestible capsules—tiny, swallowable medical devices that are revolutionizing gastrointestinal health monitoring and targeted therapy.
-

While most people think of Botox as a simple beauty treatment, there’s a surprising amount of engineering, anatomy, and precision behind the process.
-

A theranostic wound dressing does more than cover a cut—it actively detects infection and delivers targeted treatment.
-

In a sophisticated world of ever increasing complexity, we need our tools to evolve alongside us and assist in complex decision making, allowing us to understand the consequences of choices ahead. Computational Modelling and Simulation (CM&S) is emerging as an essential tool in building evidence for medical device development.
-

In this episode of MedDevice by Design, we follow the development journey of a transformative chest therapy device for cystic fibrosis patients. Host Mark Drlik introduces a voice coil prototype from an early-stage project that would eventually evolve into the Hill-Rom Monarch—a commercial system delivering high-frequency chest wall oscillation therapy.
-

I routinely engage in the development of prototype medical devices. These prototypes typically incorporate at least one printed circuit board (PCB) installed within a plastic or metal enclosure, featuring numerous connections to external components through various connectors.
-
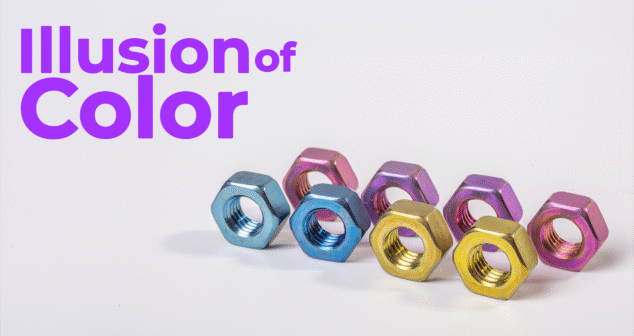
We explore the fascinating intersection of materials science and usability in medical device development. Mark Drlik and Ariana Wilson discuss how anodized titanium produces vibrant color without dyes, and how this visual property supports surgical safety, device differentiation, and biocompatibility.
-

Nick and Joris break down what a DHF is, why it's required, and how it plays a vital role throughout the development lifecycle.
-
Nick Allan and Joris van der Heijden revisit one of StarFish Medical’s most successful Pathfinder journeys, showcasing how a bold research concept evolved into a fully realized clinical diagnostic device.