
Bio Break: Understanding Continuous Glucose Monitors
Continuous glucose monitors (CGMs) are revolutionizing how people track blood sugar levels in real time. But how do they work, and where exactly do they measure glucose? In this episode of Bio Break, Nick and Joris explore the science behind CGMs, explaining the difference between blood glucose monitoring and interstitial fluid measurement—and why CGMs don’t actually draw blood continuously.
Rather than inserting a sensor directly into a vein, CGMs use microneedles or tiny tubes that sit in the interstitial fluid, the liquid surrounding the body’s cells. Unlike blood, which flows within veins, interstitial fluid is more accessible for continuous monitoring. However, there’s a key tradeoff—glucose levels in interstitial fluid lag behind blood glucose levels by about 5-10 minutes. This means CGMs don’t provide an instant blood sugar reading but rather a near-real-time estimate.
Nick raises an important question: does this time lag matter for diabetes management or sports performance tracking? Joris explains that while this delay exists, CGMs still offer huge advantages over traditional blood testing, which often requires finger pricks or lab draws that provide only a single data point. The ability to continuously measure glucose, lactate, or other small molecules gives users a clearer picture of how their body responds to food, exercise, and lifestyle changes.
However, not everything can be measured using interstitial fluid. Large molecules like hormones, red blood cells, and protein-bound compounds don’t diffuse as easily into interstitial fluid, making them difficult to track with a CGM. But for small molecules such as glucose, lactate, histamine, and creatinine, interstitial fluid monitoring is a powerful tool for real-time insights into metabolism.
If you’ve ever wondered how CGMs work or why they don’t require direct blood sampling, this episode breaks down the technology in a simple, engaging way.
Understanding Continuous Glucose Monitors
Related Resources

Antibiotics changed medicine forever, but many people still wonder how penicillin works at a biological level. Nick and Nigel break down the science behind one of the most important antibiotics ever discovered.

Nick and Nigel explore how much bacteria can exist on devices and why it matters. They explain that bacteria are everywhere.
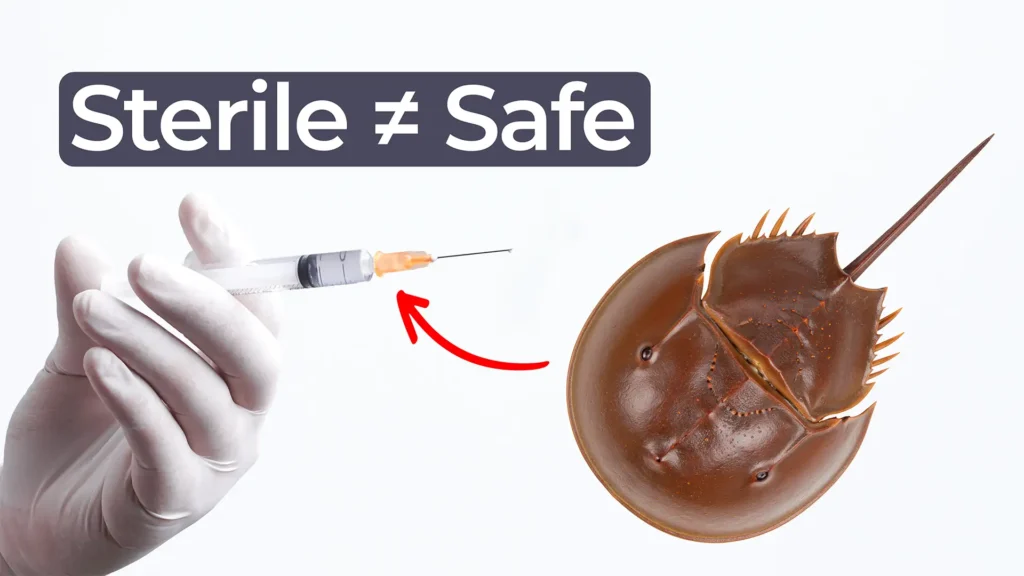
Bacterial endotoxin testing plays a critical role in medical device safety. In this Bio Break episode, Nick and Nigel take a surprising path from aliens and crabs to one of the most important quality checks in MedTech.
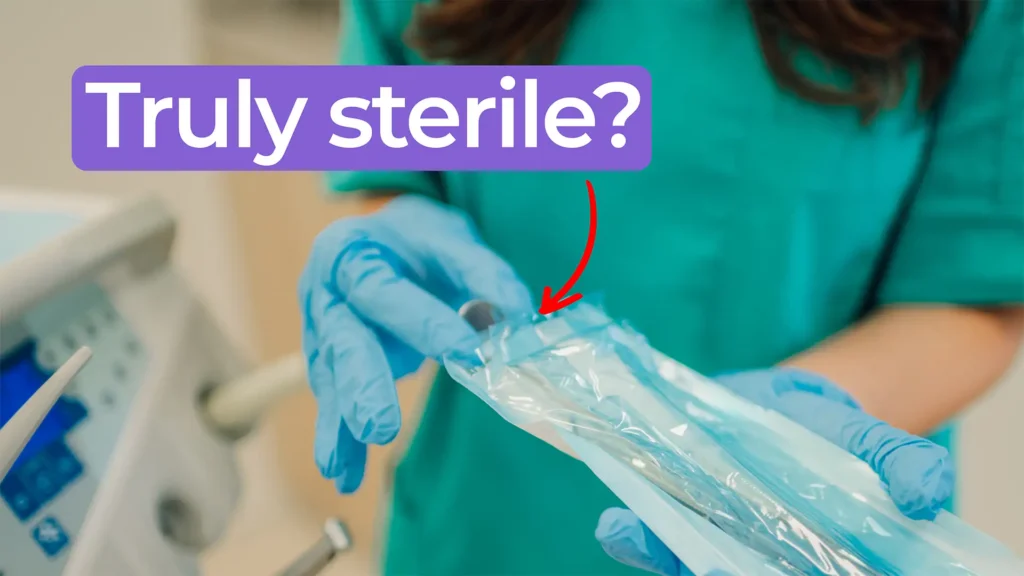
Nick and Nigel walk through how sterile disposables are processed and verified before they reach the field.
